Introduction:
Black holes are one of the most mysterious and fascinating phenomena in the universe. These objects are so dense that nothing, not even light, can escape their gravitational pull. In this blog, we will delve into the world of black holes, their properties, and the effects they have on the universe.
What are Black Holes?
Black holes are formed when a massive star runs out of fuel and collapses under its own gravity. The resulting object is so dense and has such a strong gravitational pull that anything that gets too close is sucked in, including light. The point of no return, beyond which nothing can escape, is known as the event horizon.
Types of Black Holes:
Black holes can be classified into three types: stellar, intermediate, and supermassive. Stellar black holes are formed when a star collapses, and they have a mass ranging from a few to tens of times the mass of the sun. Intermediate black holes have a mass between 100 and 100,000 times that of the sun and are thought to be formed by the merging of smaller black holes. Supermassive black holes, on the other hand, have a mass of millions to billions of times that of the sun and are thought to exist at the centers of most galaxies.
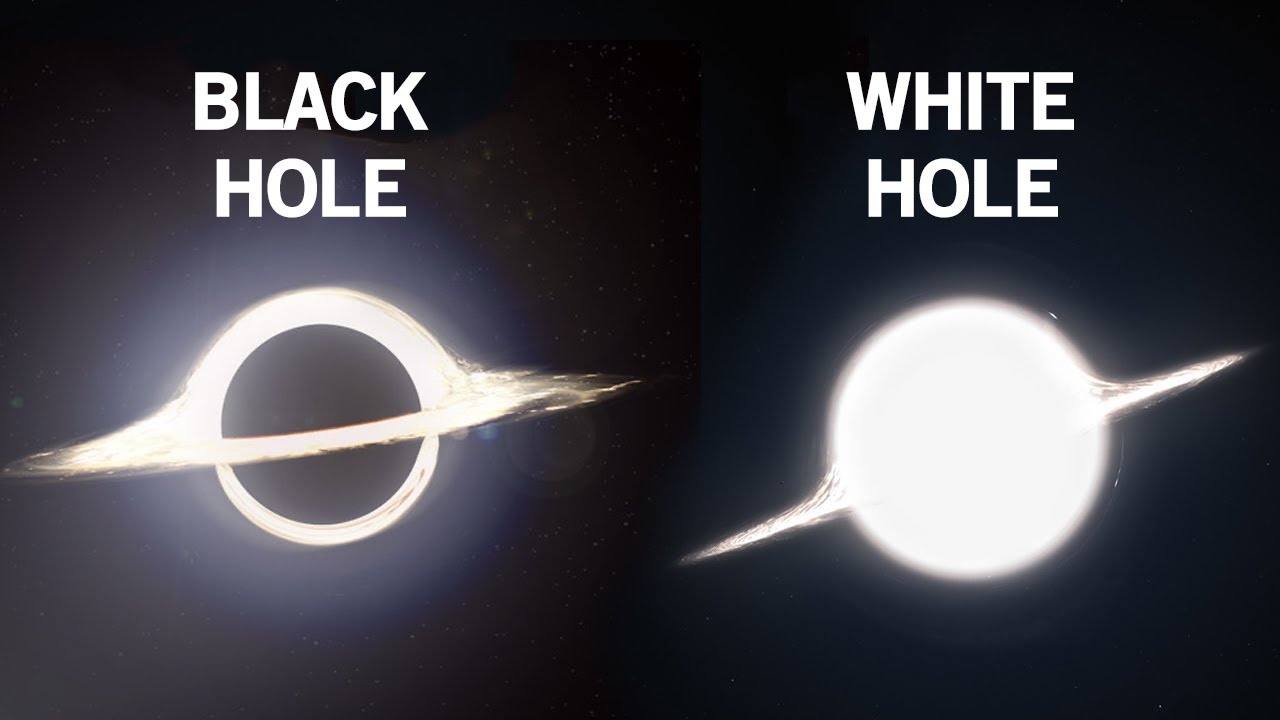
Black and White Holes:
While black holes are known for their ability to suck in everything around them, there is also the theoretical possibility of white holes. White holes are the opposite of black holes, where nothing can enter them, but everything that has entered the event horizon of a black hole is ejected out. However, there is no direct observational evidence of white holes to date.
Properties of Black Holes:
Black holes are defined by three properties: mass, spin, and charge. Mass is the amount of matter in the black hole, spin is the rotation of the black hole, and charge is the electrical charge of the black hole. The properties of a black hole determine its behavior, such as how fast it spins and how strong its gravitational pull is.
Effect on the Universe:
Black holes have a significant impact on the universe. They are responsible for the formation of galaxies and the distribution of matter in the universe. As matter is pulled into a black hole, it heats up and emits radiation. This radiation can be observed by astronomers and is an important tool for studying black holes.
Conclusion:
Black holes are fascinating objects that have captured the imagination of scientists and the public alike. While much remains to be discovered about these enigmatic phenomena, they play an essential role in shaping the universe as we know it. With new technologies and observations, we can continue to explore the mysteries of black holes and learn more about their properties and effects on the universe.