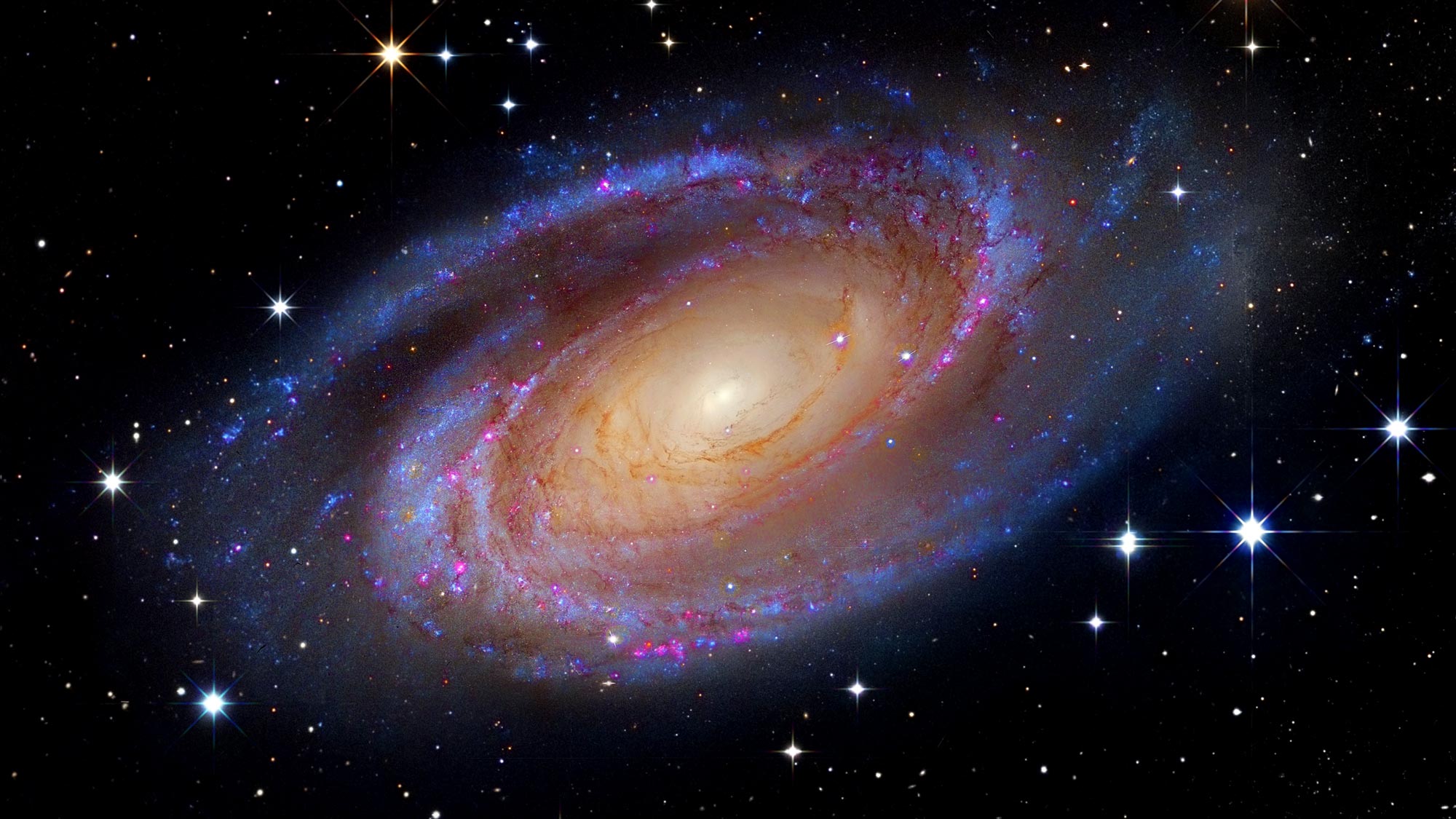
The Milky Way and Andromeda are the two largest galaxies in the Local Group, a cluster of more than 50 galaxies that includes our own. They are also on a collision course with each other, and in about 4 billion years, they will merge to form a new galaxy that astronomers have dubbed "Milkomeda."
The idea of a galactic merger might sound like something out of science fiction, but it is actually a common occurrence in the universe. Galaxies are constantly moving and interacting with each other due to the gravitational forces between them. Over time, some of them will collide and merge, forming larger and more complex structures.
The merger of the Milky Way and Andromeda is expected to be one of the most spectacular astronomical events in the history of our galaxy. It will take billions of years to complete, and it will reshape the entire structure of the Milky Way.
What will happen during the merger?
The merger of the Milky Way and Andromeda will be a slow and gradual process that will take place over billions of years. However, it will have a significant impact on the structure and composition of both galaxies.
As the two galaxies approach each other, their gravitational forces will cause them to distort and elongate. Eventually, they will merge into a single, larger galaxy. This new galaxy will be a mix of the two original galaxies, with stars, gas, and dust from both contributing to its composition.
The merger will also trigger a massive burst of star formation. The gas and dust that are compressed during the collision will collapse to form new stars, and the resulting increase in the number of stars in the galaxy will lead to a much brighter and more massive object.
The merger will also cause the black holes at the centers of both galaxies to merge. This will produce a much larger and more powerful black hole, which will continue to grow over time as it consumes matter from its surroundings.
What will be the impact on Earth?
Despite the dramatic nature of the Milky Way-Andromeda merger, its impact on Earth is likely to be minimal. The distance between our solar system and the nearest stars in the two galaxies is so vast that the chances of a collision are almost zero.
However, the merger will have a profound impact on the night sky as seen from Earth. As the two galaxies merge, their stars will be thrown into new orbits, and the resulting changes in their positions will lead to a dramatic restructuring of the Milky Way.
Over time, the Milky Way will absorb many of the stars from Andromeda, resulting in a much larger and more complex galaxy. This will also change the appearance of the night sky, as the distribution of stars will be different from what we see today.
Conclusion
The merger of the Milky Way and Andromeda is an event that is likely to take place billions of years from now, but it is a reminder that the universe is a dynamic and ever-changing place. The resulting galaxy, Milkomeda, will be a complex and fascinating object that will challenge our understanding of the universe.
As astronomers continue to study the Milky Way and Andromeda, they will gain a better understanding of the processes that govern the behavior of galaxies. This knowledge will be invaluable as we seek to understand the origins and evolution of the universe itself.
The merger of the Milky Way and Andromeda is a reminder that even the largest and most stable objects in the universe are subject to change. It is a reminder that we are all part of a much larger and more complex system, and that the universe is full of surprises and wonders that we have yet to discover.