The fourth dimension refers to a hypothetical spatial dimension beyond the three dimensions of length, width, and height that we are familiar with in our everyday lives. It is a mathematical concept used to model and explain certain phenomena in physics, such as the behavior of subatomic particles and the curvature of spacetime.
The idea of a fourth dimension can be difficult to grasp because it is not directly observable in our physical reality. However, it is often represented and visualized mathematically through the use of coordinate systems and geometric shapes such as the hypercube or tesseract.
In popular culture, the fourth dimension is often used in science fiction to represent alternate realities, time travel, or other supernatural or futuristic concepts. However, it is important to note that these depictions are typically not based on scientific fact or theory.
In physics and mathematics, the fourth dimension refers to a hypothetical fourth spatial dimension that is perpendicular to the three dimensions of length, width, and height that we are familiar with in our everyday lives.
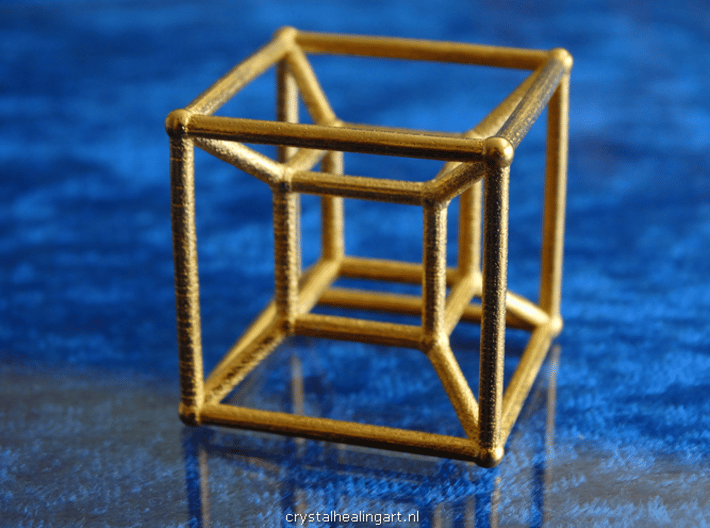
In a geometrical sense, the concept of a fourth dimension is often used to describe the position and movement of objects in space beyond the three dimensions that we can see and interact with. One common way to visualize the fourth dimension is through the use of a "hypercube," also known as a "tesseract," which is a four-dimensional cube that has eight cubical cells.
As the fourth dimension is a mathematical concept, it is not directly observable in our physical reality. However, it is a useful tool in physics and mathematics for modeling and explaining certain phenomena. Here are some examples of the fourth dimension in these fields:
Time: Time is often considered the fourth dimension in physics, as it is a dimension in which objects and events occur and can be measured. The concept of spacetime combines the three dimensions of space with time as the fourth dimension.
Quantum mechanics: In quantum mechanics, the wave function is often represented as a complex function in a four-dimensional space, with three dimensions representing space and the fourth dimension representing time.
General relativity: In general relativity, the curvature of spacetime is often represented in four dimensions, with three dimensions representing space and the fourth dimension representing time.
Hypercubes: A hypercube, also known as a tesseract, is a geometric shape that exists in four dimensions. It is a cube-like object with eight cubes as its faces, and is often used to visualize the concept of the fourth dimension in geometry and mathematics.
It's important to note that the concept of a fourth dimension is purely theoretical and not directly observable in our physical reality. However, it is a useful concept in fields such as physics and mathematics, where it is used to model complex systems and phenomena that cannot be fully explained by the laws of three-dimensional space.