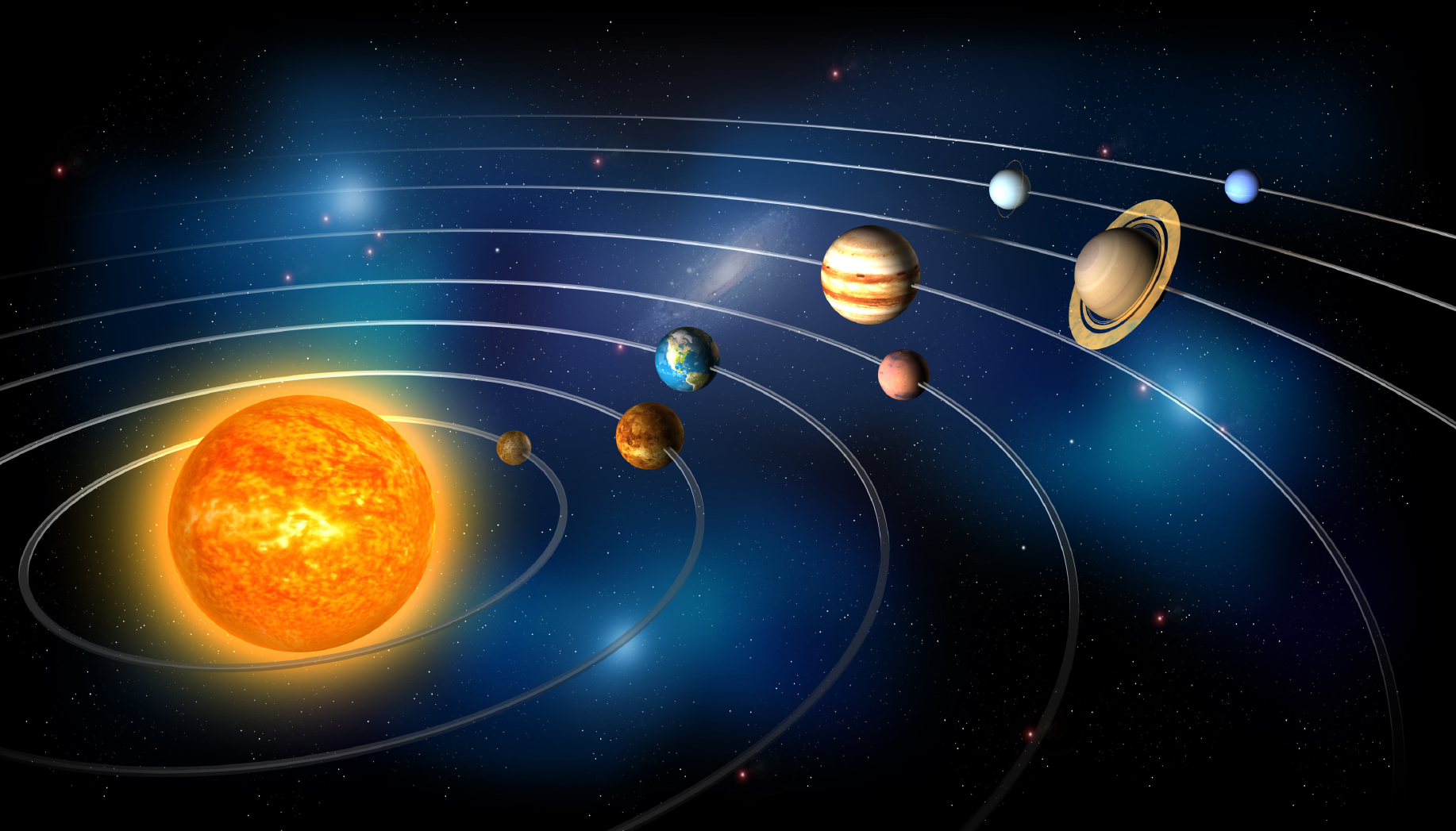
The Solar System is the planetary system that comprises our Sun and all the celestial objects that orbit around it. It is a vast expanse of space that has fascinated humans for centuries. In this blog, we will explore the size of the Solar System and its various components.
The Sun, at the center of the Solar System, is a massive ball of gas and plasma, with a diameter of about 1.4 million kilometers. Its mass accounts for 99.86% of the total mass of the Solar System. The Sun's enormous size and energy production are what make life on Earth possible. The Sun is the driving force behind the Solar System's formation and evolution.
The first planet in the Solar System is Mercury, which is also the smallest. It has a diameter of only 4,880 kilometers, which is less than one-third the size of Earth. Mercury is the closest planet to the Sun, with an average distance of about 58 million kilometers. Due to its proximity to the Sun, Mercury has a surface temperature that can reach up to 430°C during the day and drop to -180°C at night.
The second planet from the Sun is Venus, which is similar in size to Earth, with a diameter of about 12,104 kilometers. Venus is the hottest planet in the Solar System, with a surface temperature that can reach up to 470°C due to its thick atmosphere. Venus is also the brightest object in the night sky after the Moon, making it visible to the naked eye.
Earth, the third planet from the Sun, is the largest of the four terrestrial planets. It has a diameter of about 12,742 kilometers and is the only planet in the Solar System known to support life. Earth has a stable climate and a magnetic field that protects it from the solar wind, making it an ideal place for living organisms to thrive.
The fourth planet from the Sun is Mars, also known as the Red Planet, due to its reddish appearance in the sky. Mars has a diameter of about 6,779 kilometers and is similar in size to Mercury. Mars has polar ice caps, a thin atmosphere, and evidence of liquid water on its surface, making it a prime target for future exploration.
After the four terrestrial planets comes the Asteroid Belt, which is a region between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. The Asteroid Belt contains millions of small rocky and metallic objects, some of which are large enough to be classified as dwarf planets. The largest object in the Asteroid Belt is Ceres, which has a diameter of about 940 kilometers and was recently reclassified as a dwarf planet.
Jupiter, the fifth planet from the Sun, is the largest planet in the Solar System. It has a diameter of about 139,822 kilometers, which is more than ten times the size of Earth. Jupiter is a gas giant and has a strong magnetic field that generates intense radiation belts around the planet. Jupiter also has four large moons, known as the Galilean moons, which were discovered by Galileo Galilei in 1610.
Saturn, the sixth planet from the Sun, is known for its beautiful rings, which are made up of ice particles and rocky debris. Saturn has a diameter of about 116,460 kilometers and is almost as large as Jupiter. Saturn is also a gas giant and has numerous moons, including Titan, the only moon in the Solar System with a dense atmosphere.
Uranus, the seventh planet from the Sun, is an ice giant and has a diameter of about 50,724 kilometers. Uranus has a tilted axis of rotation, which causes its seasons to be extreme and last for over 20 years. Uranus has numerous moons, and its largest moon, Miranda, has a unique surface that is covered in deep can yons and ridges.
Neptune, the eighth and farthest planet from the Sun, is also an ice giant with a diameter of about 49,244 kilometers. Neptune has a dynamic atmosphere with storms and winds that are some of the strongest in the Solar System. Neptune has thirteen known moons, including Triton, which is the largest and coldest moon in the Solar System.
Beyond Neptune lies the Kuiper Belt, which is a region of the Solar System that contains icy objects such as dwarf planets, comets, and asteroids. The most famous object in the Kuiper Belt is Pluto, which was discovered in 1930 and was considered the ninth planet in the Solar System until its reclassification as a dwarf planet in 2006. Pluto has a diameter of about 2,377 kilometers and has five known moons.
The Solar System is vast, and its size can be measured in various ways. One way to measure the size of the Solar System is by its distance from the Sun. The average distance between the Sun and Earth is about 150 million kilometers, which is also known as one astronomical unit (AU). The distance between the Sun and the farthest known object in the Solar System, which is the dwarf planet Eris, is about 96 AU.
Another way to measure the size of the Solar System is by its volume. The Solar System's volume is estimated to be about 8.24×10¹¹ cubic astronomical units (AU³). To put that into perspective, if the Sun were the size of a basketball, the entire Solar System would be about the size of a football field.
In conclusion, the Solar System is a vast and fascinating expanse of space that is home to our Sun, eight planets, numerous dwarf planets, moons, comets, and asteroids. Each of these celestial objects is unique and plays a crucial role in the formation and evolution of the Solar System. Understanding the size and characteristics of the Solar System is essential to our understanding of our place in the universe and our ongoing exploration of space.