Jupiter is the largest planet in our solar system and is one of the five planets visible to the naked eye from Earth. It is a gas giant, meaning it has no solid surface, and is composed mostly of hydrogen and helium gas. In this blog, we will delve into the age, discovery, moons, atmosphere, wind speed, gases of Jupiter, gravity, mass, depth, size with examples, the giant red spot with age, cold spot, and ten fascinating facts about the colossal king of the solar system.
Age and Discovery of Jupiter
Jupiter is estimated to be around 4.5 billion years old, which is about the same age as the Sun and the rest of the solar system. It is named after the Roman king of gods and was discovered in 1610 by Galileo Galilei when he observed the four largest moons of Jupiter, now known as the Galilean moons.
Moons of Jupiter
Jupiter has a total of 92 known moons, with the four largest being Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto. These moons are collectively known as the Galilean moons, named after their discoverer. These four moons are the largest moons in the solar system and are each unique in their own way. Io is the most volcanically active object in the solar system, Europa is believed to have a subsurface ocean, Ganymede is the only moon in the solar system with its own magnetic field, and Callisto is the third-largest moon in the solar system.
Atmosphere and Wind Speed of Jupiter
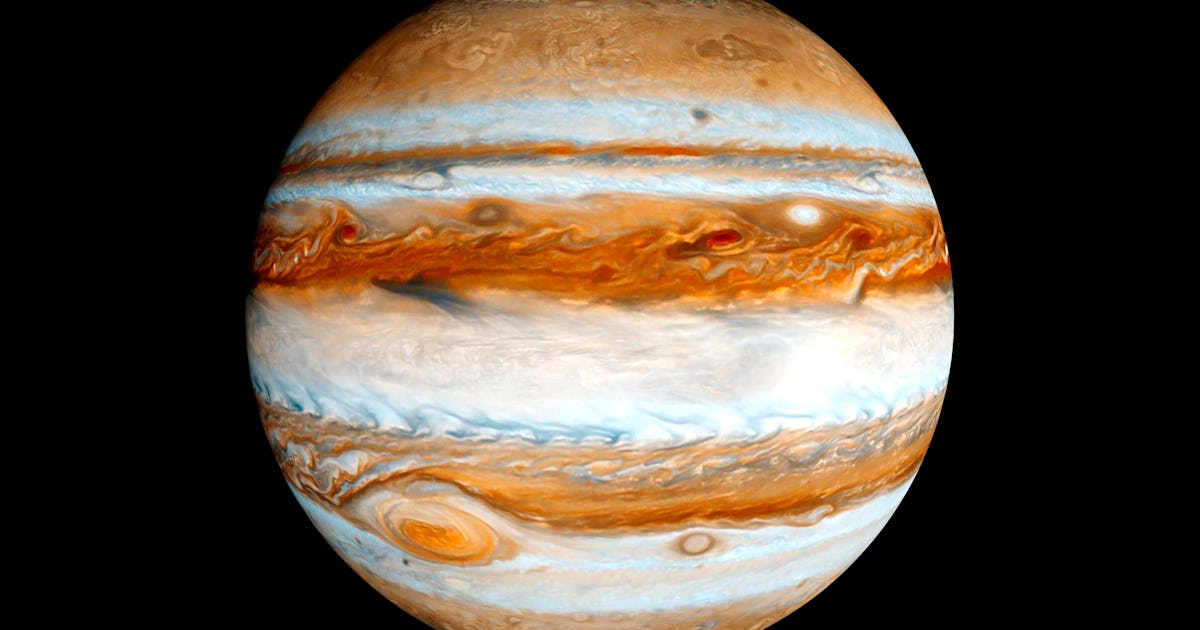
Jupiter's atmosphere is composed mainly of hydrogen and helium gas, with trace amounts of other elements such as methane, ammonia, and water vapor. The atmosphere is characterized by its alternating bands of light and dark clouds, with the lighter bands known as zones and the darker bands known as belts. Jupiter also experiences the fastest wind speeds in the solar system, with wind speeds reaching up to 384 miles per hour (618 kilometers per hour) in some areas.
aspect, let's talk about the atmosphere of Jupiter. The atmosphere of Jupiter is made up mostly of hydrogen and helium gases. It also has small amounts of methane, water vapor, and ammonia. The clouds in Jupiter's atmosphere are made up of ammonia crystals and other compounds. These clouds give Jupiter its distinct, colorful appearance.
The winds on Jupiter are incredibly strong and can reach speeds of up to 400 miles per hour (644 kilometers per hour). These winds are caused by the planet's rapid rotation, which takes just under 10 hours to complete. This rotation also causes the equator to bulge out, making Jupiter the most oblate planet in the solar system.
Jupiter's atmosphere is primarily composed of hydrogen gas, which makes up about 75% of its total mass, and helium gas, which makes up about 24% of its total mass. Other gases that have been detected in Jupiter's atmosphere include methane, ammonia, water vapor, and trace amounts of other gases such as ethane, phosphine, and hydrogen sulfide.
Gravity, Mass, and Depth of Jupiter
Jupiter's massive size gives it a strong gravitational pull, which is about 2.5 times that of Earth's gravity. Its mass is about 318 times that of Earth, making it the largest planet in the solar system. The depth of Jupiter's atmosphere is estimated to be about 1,000 kilometers (620 miles), after which the pressure and temperature increase to the point where the gases become a liquid.
Jupiter's mass is 1.898 x 1027 kg, making it the largest planet in the solar system. Its gravity is also the strongest, with a surface gravity of 24.79 m/s2. The planet's size is so massive that it could fit all of the other planets in the solar system inside it. For example, Jupiter's diameter is 86,881 miles (139,822 kilometers), which is more than 11 times the diameter of Earth.
Jupiter's interior is made up of layers of gas, with the outermost layer being hydrogen gas. This layer is so thick that it becomes metallic near the core, which means that it conducts electricity. The exact depth of Jupiter's atmosphere is unknown, but it is estimated to be around 1,000 kilometers (620 miles) deep.
The Giant Red Spot and Cold Spot
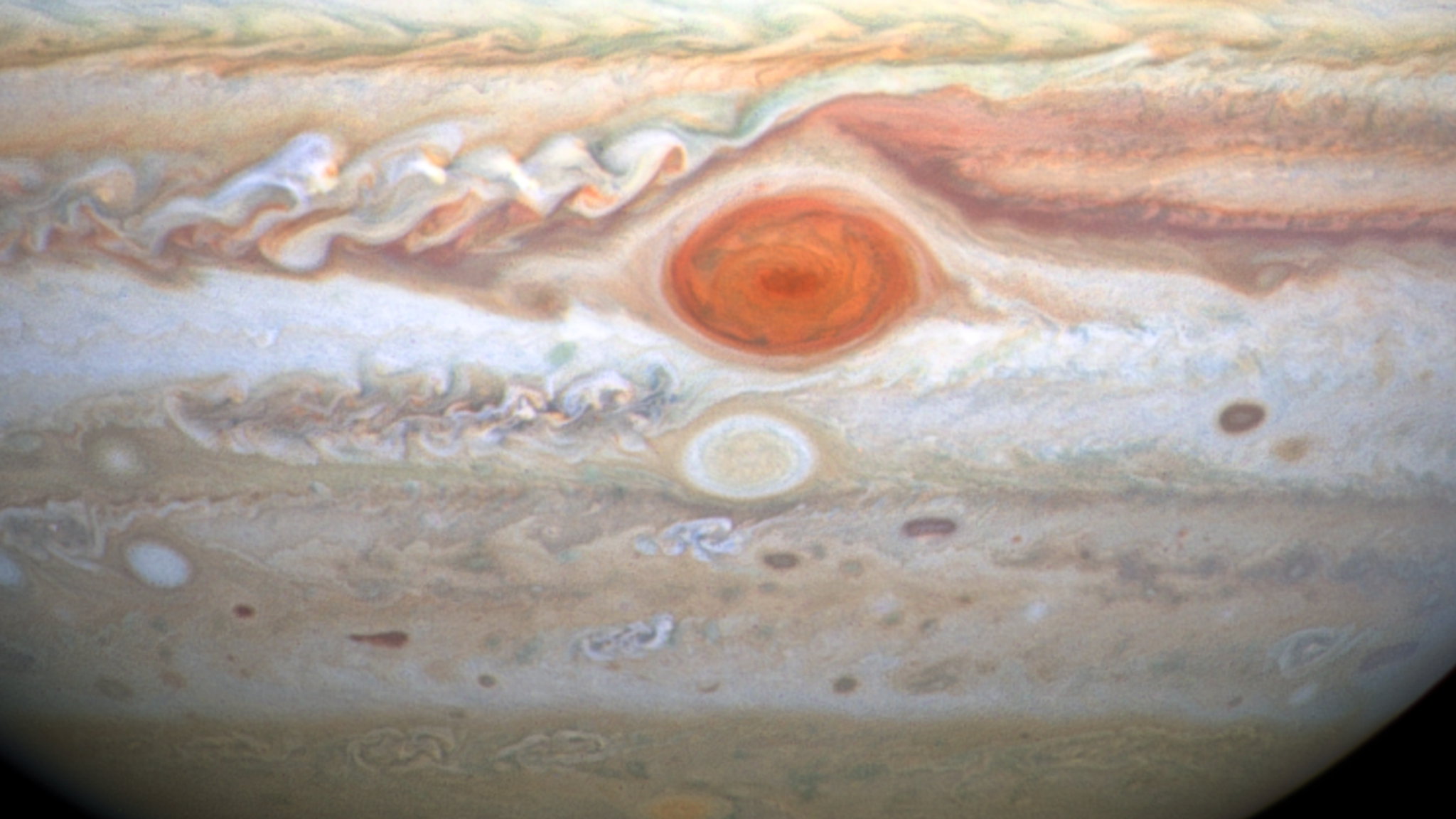
One of the most famous features of Jupiter is the Great Red Spot, which is a giant storm that has been raging for at least 400 years. This storm is so large that it could fit two or three Earths inside of it. However, in recent years, the Great Red Spot has been shrinking, and it is unclear whether it will continue to exist for much longer.
Here are ten more facts about Jupiter:
- Jupiter is named after the Roman king of the gods.
- Jupiter has more than 80 moons, with the four largest being Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto.
- Ganymede is the largest moon in the solar system and is larger than the planet Mercury.
- Jupiter is often called a failed star because it did not have enough mass to become a star.
- Jupiter has a strong magnetic field that is 14 times stronger than Earth's.
- The first spacecraft to visit Jupiter was Pioneer 10 in 1973.
- The Galileo spacecraft, which orbited Jupiter from 1995 to 2003, discovered that Europa has an ocean beneath its icy surface.
- Jupiter has a faint ring system.
- Jupiter is one of the five planets visible from Earth with the naked eye.
- Jupiter has a very short day, with one day on Jupiter lasting less than 10 hours.
In conclusion, Jupiter is a fascinating planet that has captured the imaginations of people for centuries. From its massive size and strong gravity to its colorful atmosphere and giant storms, Jupiter is a planet that continues to surprise and intrigue scientists and space enthusiasts alike. With ongoing research and exploration, we are sure to learn even more about this incredible planet in the years to come.
Test Quiz
MCQs
Short Questions
© copyright 2023 - blogger content