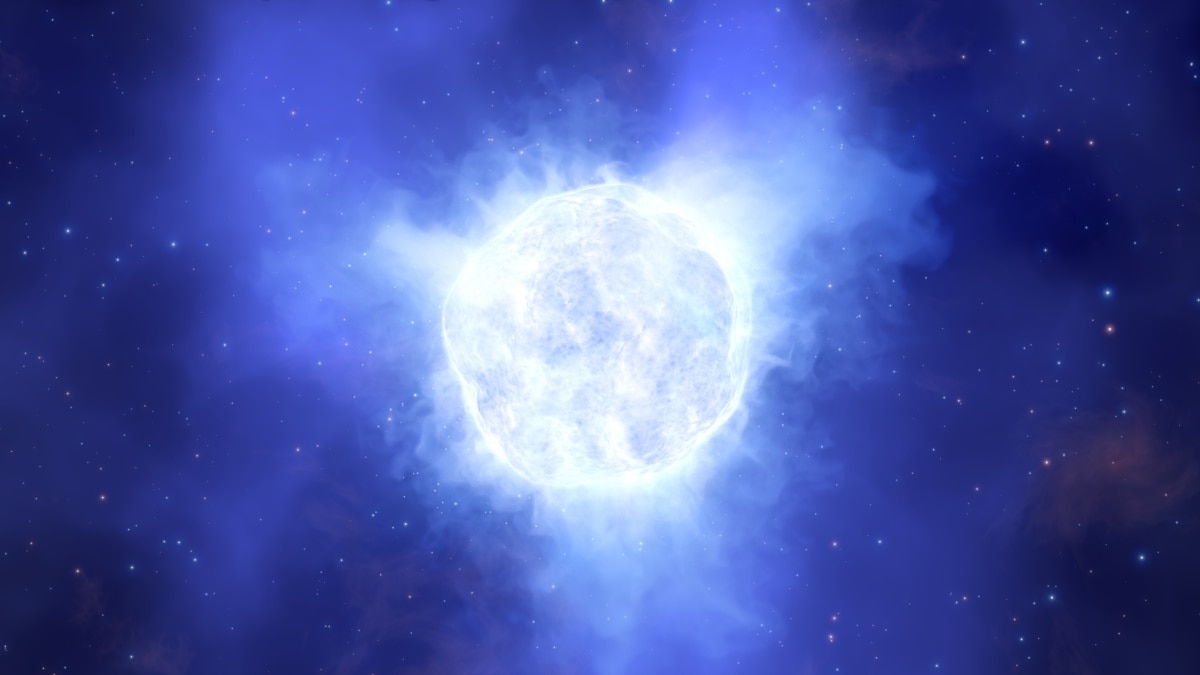
Massive stars are some of the most fascinating objects in the universe. They are born from the collapse of giant clouds of gas and dust, and they live fast and die young. As they evolve, they undergo a series of dramatic changes, culminating in a spectacular supernova explosion or the formation of a black hole. In this article, we will explore the evolution and fate of massive stars, and how they ultimately end their lives as supernovae or black holes.
Massive stars are born from the collapse of giant clouds of gas and dust. As the cloud collapses, it forms a protostar, which is a dense, hot core of gas and dust. As the protostar continues to collapse, it heats up and begins to emit light. This is the birth of a massive star.
As the star continues to evolve, it begins to fuse hydrogen into helium in its core. This process releases energy, which is radiated away from the star's surface. As the star continues to fuse hydrogen, it begins to expand and cool. This is the main sequence phase of the star's life.
Eventually, the star will run out of hydrogen fuel and begin to fuse heavier elements in its core. This process releases even more energy, causing the star to expand and cool even further. This is the red giant phase of the star's life.
At this point, the star's core is so hot and dense that it can no longer support itself. The core collapses, triggering a massive explosion known as a supernova. The supernova is so powerful that it can outshine an entire galaxy. The star's outer layers are blasted away, leaving behind a dense core of matter known as a neutron star or a black hole.
Neutron stars are incredibly dense objects, with a mass of up to three times that of the Sun. They are composed of tightly packed neutrons, and they are incredibly hot. Black holes, on the other hand, are even more mysterious. They are regions of space-time where gravity is so strong that nothing, not even light, can escape.
The evolution and fate of massive stars is an incredible story of birth, life, and death. From the collapse of a giant cloud of gas and dust to the formation of a supernova or black hole, massive stars have a dramatic and fascinating life cycle. In the end, they leave behind a legacy of light and energy that will continue to shape the universe for billions of years to come.
Conclusion:
Massive stars are some of the most fascinating objects in the universe. They are born from the collapse of giant clouds of gas and dust, and they live fast and die young. As they evolve, they undergo a series of dramatic changes, culminating in a spectacular supernova explosion or the formation of a black hole. In the end, they leave behind a legacy of light and energy that will continue to shape the universe for billions of years to come.